Telegram CEO Arrest, revisited
Geopolitics of Messenger Apps
Published: September 11, 2025
Why are messenger apps important?
Control over information: whoever owns the platform can influence or potentially control the flow of human communication.
Security and surveillance: governments are interested in messaging data, for crime prevention and spying on citizens.
Sovereignty: states want to be independent of overseas influence which can come from foreign-owned platforms of communication.
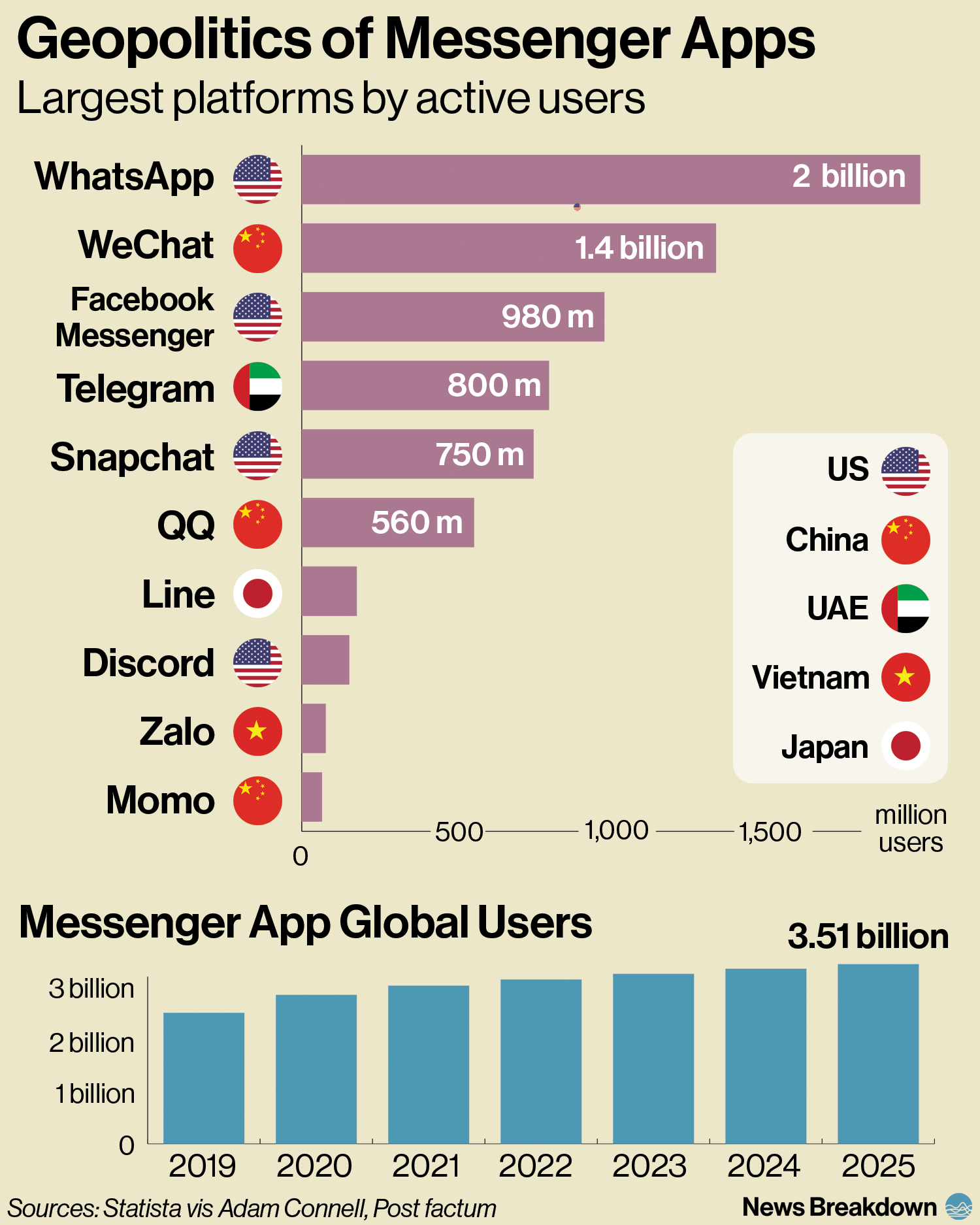
Over 3.5 billion people use messenger apps.
WhatsApp is the largest platform with around 2 billion active users. It is owned by US-based Meta (Facebook).
WeChat, the Chinese super app, is the second largest platform with around 1.3 billion users.
A super app (or an everything app) combines messaging with other functions like payments, shopping and social media.
WeChat is legally required to share data with the Chinese state and has integrated censorship mechanisms.
Messenger apps play a key role in citizens’self-organisation for political protests and grassroots movements.
A grassroots movement is a collective effort of ordinary people at a local level to create social change.
Encryption
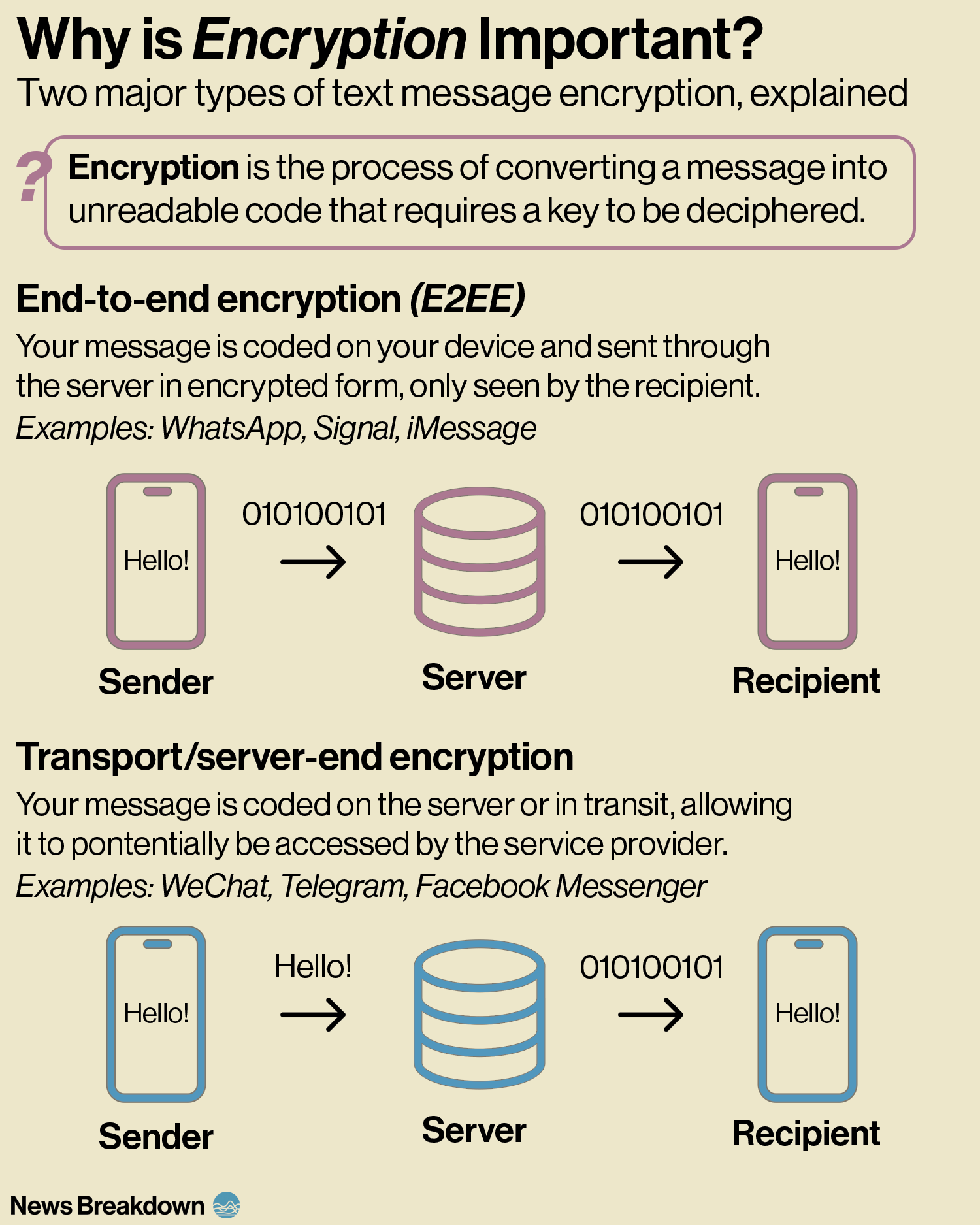
Messenger apps can encrypt messages: convert them into code to hide the content from hackers or surveillance.
A key factor is when encryption takes place:
End-to-end encryption: the message is converted into code on your device, then sent through the server to the recipient. The message is then converted back on the recipient’s device.
Transport encryption: the message is encrypted on its way from the device to the app’s server. This allows the message to be accessed from the server.
WhatsApp uses end-to-end encryption (E2EE) in all its chats.
In 2013, an intelligence services contractor, Edward Snowden, revealed US government’s large-scale efforts to collect messaging and other private data globally.
The resulting backlash was one of the reasons for WhatsApp adoption of E2EE protocols.
However, the US government still has the ability to access some communications data through both legal and hacking methods.
WeChat does not use end-to-end encryption, instead using a custom transport encryption protocol. This allows China to access user data.
Chinese law requires all companies to store data locally and provide access on request.
The European Union does not have a domestic messenger app.
However, it has stricter regulation of messenger apps and other digital platforms on privacy and security.
International tech companies have previously been fined billions of dollars for breaching European regulations on data privacy, business rules and other.
Telegram and Pavel Durov
Telegram is the world’s 4th largest messenger app, and the fastest growing one in 2024.
It does not use E2EE in its regular chats but allows it to be turned on with the “secret chats” function.
Telegram is particularly popular in Eastern Europe and some countries in Eurasia, like Kazakhstan and Armenia.
In Europe and the West it has a reputation for being used for illicit activity like selling drugs or private data.
Telegram was founded in Russia by Nikolai and Pavel Durov but is now based in Dubai (UAE).
Pavel Durov previously founded VK, Russia’s largest social network. He left the company in 2014 after a conflict with intelligence services over revealing private data of protesters in Russia and Ukraine.
Telegram was banned by Russia in 2018.
However, after unsuccessful attempts to bring the service offline and an agreement with the platform to share some data through legal requests, the ban was removed.
In August 2024, Pavel Durov was arrested in France.
He was charged with complicity in (involvement with) drug trafficking, distribution of child pornography and other crimes.
If found guilty, Durov faces up to 20 years in prison. More than a year later, the investigation is still ongoing.
For most of this time, he was banned from leaving France.
Since July 2025, Durov is allowed to leave France for 2 weeks at a time, with approval.
His trip home to Dubai was approved but an investment meeting trip to the US was denied.
[UPDATE: in November 2025 all travel restrictions were removed, but the investigation is still ongoing.]
Durov stands trial as a French citizen. He also holds the citizenships of Russia, United Arab Emirates, and Saint Kitts and Nevis (an island country in the Caribbean).
This case represents a rare situation where a social platform’s founder is charged for involvement in the crimes committed on it.
Ross Ulbricht founded a darknet marketplace and later served 12 years in prison for allowing the sales of drugs, weapons and other illegal goods on the platform, before being pardoned by President Trump in 2025.
Changpeng Zhao served 4 months in prison for allowing money laundering on his cryptocurrency trading platform, Binance.
Since Durov’s arrest, Telegram has made changes to its policies on removing harmful materials and sharing some data of alleged criminals through legal requests.
Russia accused France of acting against freedom of speech, and in a politically motivated manner.
In June 2025, Russia announced the release of an official national messenger app.
The messenger is created to be similar to Telegram, and is intended to become a super app, integrating with Russian social services and other digital systems.
Russia took active measures to boost the adoption of the new app and transition of users from its foreign competitors.
Marketing: the messenger is heavily promoted with state-backed funding.
Legal: ban on Telegram was re-introduced in some regions.
Technical: Russia uses its ability to control the speed of traffic on select websites to slow down WhatsApp and Telegram.
Administrative: state corporations, government workers, schools and public organisations are asked to use the new national messenger.
Other authoritarian states, like Iran, are also increasingly building and promoting local digital infrastructure for messaging, payments and other online activity.
States are increasingly concerned for the security of their communications systems.
In countries like India, Brazil or Israel, popular messengers like WhatsApp are facing increasing pressure to store data locally and share more information with authorities.
Thank you for reading!
Author Finlay Dunseath
Editor Anton Kutuzov